Running a Process
#include <psProcess.hpp>
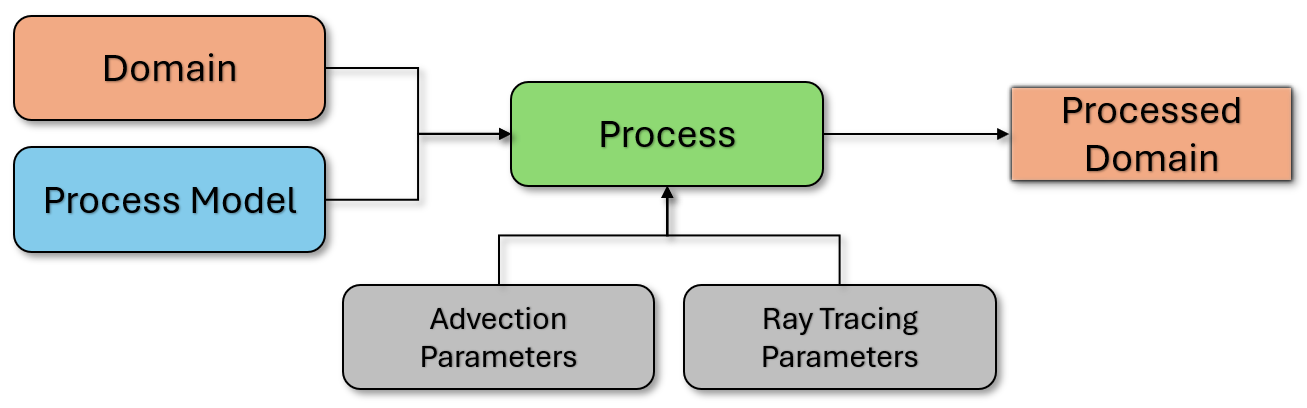
The Process class is the main simulation interface. It holds the domain, the process model, the duration, and advanced parameters. Configure it, then call apply(). The passed domain is modified in place.
Example usage
C++
// namespace viennaps
using T = double;
constexpr int D = 3;
auto process = ps::Process<T, D>();
process.setDomain(myDomain);
process.setProcessModel(myModel);
process.setProcessDuration(10.0);
// Flux engine selection
process.setFluxEngineType(ps::FluxEngineType::AUTO);
// Optional parameters
ps::AdvectionParameters<T> adv;
adv.timeStepRatio = 0.25;
ps::RayTracingParameters<T, D> rt;
rt.raysPerPoint = 500;
ps::CoverageParameters<T> cov;
cov.maxIterations = 10;
ps::AtomicLayerProcessParameters<T> alp;
alp.numCycles = 2;
process.setParameters(adv);
process.setParameters(rt);
process.setParameters(cov);
process.setParameters(alp);
// Run
process.apply();
Python
import viennaps as vps
process = vps.Process()
process.setDomain(myDomain)
process.setProcessModel(myModel)
process.setProcessDuration(10.0)
# Flux engine selection
process.setFluxEngineType(vps.FluxEngineType.AUTO)
# Optional parameters
adv = vps.AdvectionParameters()
adv.timeStepRatio = 0.25
rt = vps.RayTracingParameters()
rt.raysPerPoint = 500
cov = vps.CoverageParameters()
cov.maxIterations = 10
alp = vps.AtomicLayerProcessParameters()
alp.numCycles = 2
process.setParameters(adv)
process.setParameters(rt)
process.setParameters(cov)
process.setParameters(alp)
process.apply()
Process parameters
All advanced parameters are set via setParameters(...).
Flux engine
Select the flux computation method at runtime.
// C++
process.setFluxEngineType(ps::FluxEngineType::AUTO); // default
// or: CPU_DISK, GPU_DISK, GPU_LINE, GPU_TRIANGLE
# Python
process.setFluxEngineType(vps.FluxEngineType.AUTO) # default
# or: CPU_DISK, GPU_DISK, GPU_LINE, GPU_TRIANGLE
AUTO chooses CPU or GPU based on the build and whether the selected model has a GPU implementation.
Single-pass flux calculation
SmartPointer<viennals::Mesh<NumericType>> calculateFlux()
Computes flux for the current configuration and returns a mesh with flux data.
Member functions
Constructors
// Default
Process()
// From domain
Process(SmartPointer<Domain<NumericType, D>> passedDomain)
// From domain, model, and duration
template <typename ProcessModelType>
Process(SmartPointer<Domain<NumericType, D>> passedDomain,
SmartPointer<ProcessModelType> passedProcessModel,
const NumericType passedDuration = 0.)
Set the domain
void setDomain(SmartPointer<Domain<NumericType, D>> passedDomain)
Set the process model
void setProcessModel(SmartPointer<ProcessModel<NumericType, D>> passedProcessModel)
Set the process duration
void setProcessDuration(NumericType passedDuration)
Set parameters (unified)
void setParameters(const AdvectionParameters<NumericType>&)
void setParameters(const RayTracingParameters<NumericType, D>&)
void setParameters(const CoverageParameters<NumericType>&)
void setParameters(const AtomicLayerProcessParameters<NumericType>&)
Set flux engine type
void setFluxEngineType(FluxEngineType type)
Set intermediate output path
Path for writing intermediate results, if enabled. See Logging. for details.
void setIntermediateOutputPath(const std::string &path)
Run the process
void apply()
